Networking Your Custom GPT: Web Browsing vs WebPilot
Remember the times when using ChatGPT was all about typing prompts and getting answers? Well, those days are evolving fast! Now, with the advent of GPTs, even those of us who aren’t coding wizards can craft our own AI applications, boosting our productivity to new heights.
Imagine shaping an AI’s workflow like you’re piecing together a jigsaw puzzle of an app. Haven’t tried making your own GPT yet? Dive into this guide and start your journey!
👉 GPT Building for Everyone: A How-To
One huge leap GPTs have over ChatGPT 4 is their ability to gobble up your own documents as a knowledge base. Think of it: a GPT that knows your world inside out, your personal digital assistant. Dreaming of a GPT with up-to-the-minute intel? You’ll need to add networking, but remember, training for real-time updates takes time. Without it, your GPT’s knowledge is like a library with old books.
So, you’re ready to network your GPT? Two free solutions await you:
- ChatGPT’s built-in Web Browsing.
- The handy API from WebPilot.
This article tackles the big questions: How do you network your GPTs, and which method shines brighter?
Overview
If you’re looking to utilize ChatGPT for search tasks, building a dedicated GPTs solely for that purpose might not be the most efficient approach. ChatGPT 4 already comes equipped with its own networking capabilities, making it well-suited for handling straightforward tasks. For more intricate tasks, there’s a range of plugins available, which I’ve delved into in this article.
👉 Best ChatGPT Plugins for Web Browsing [with Demonstrations]
If you’re new to making GPTs tackle complex search tasks, start by experimenting with these plugins. Trust me, once you’ve seen ChatGPT struggle with complex tasks, you’ll understand why sometimes its built-in networking just doesn’t cut it.
How to Network GPTs
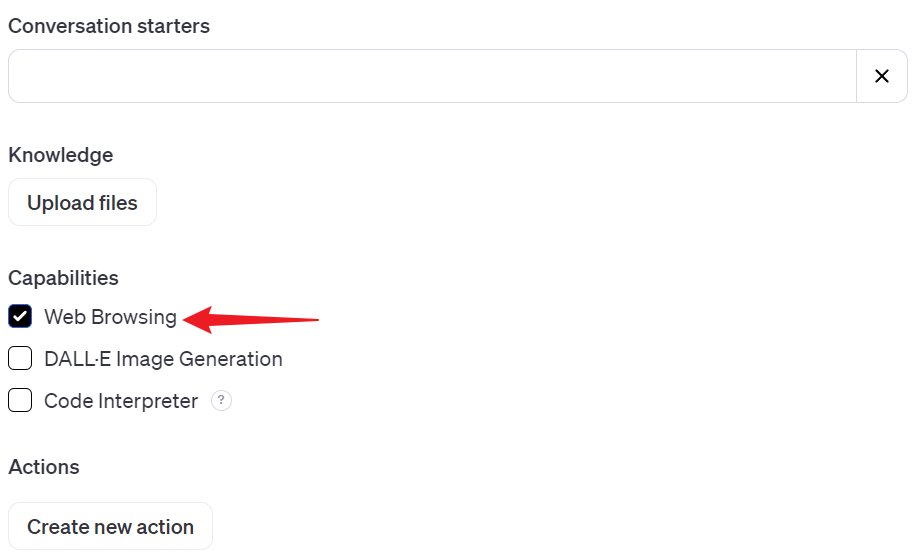
Networking your GPT is a breeze with GPTs’ features. Just tick the “Web Browsing” box.
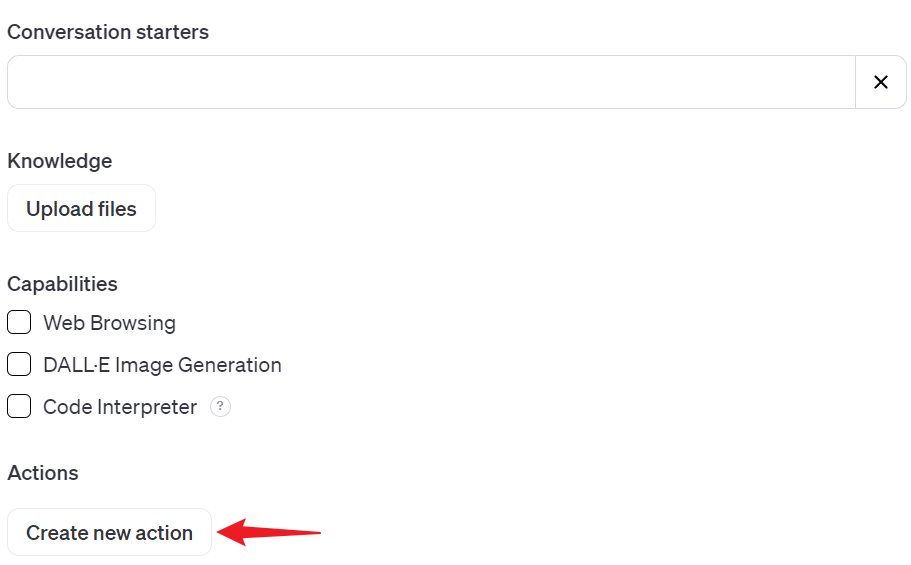
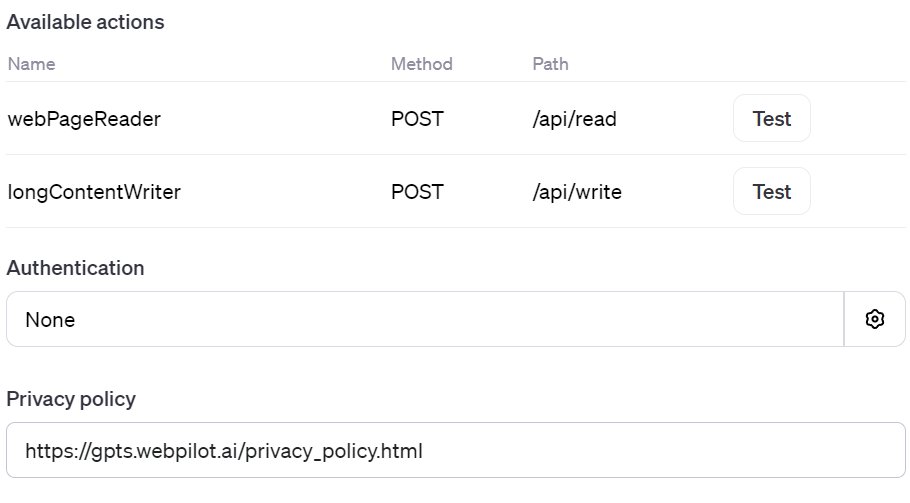
Want to try WebPilot? It’s a one-minute job to add it as an “Action”.
1️⃣ Whip up a new “Action”.
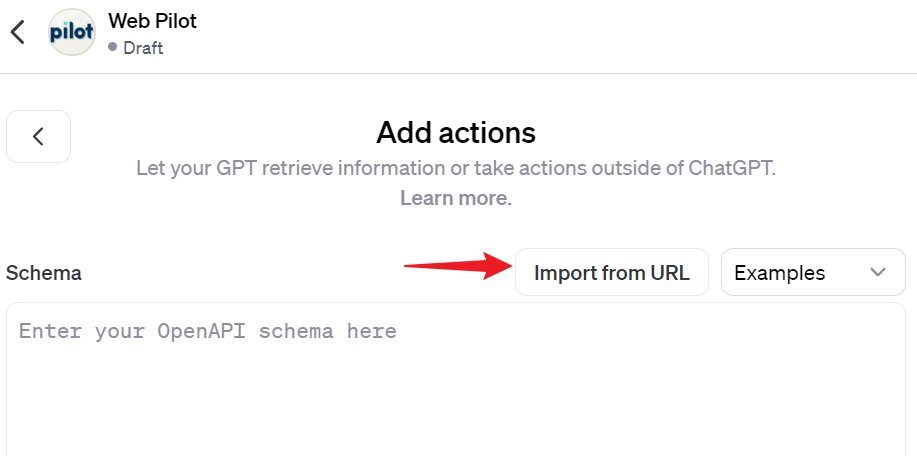
2️⃣Next, select “Import from URL” to bring in the Schema via a provided link.
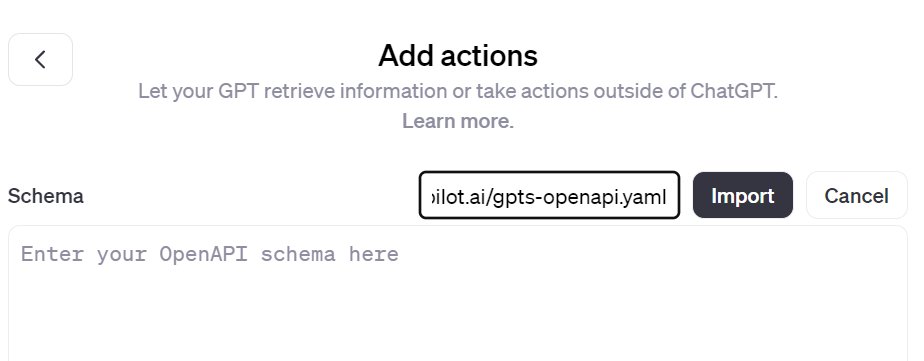
3️⃣ Enter the following link: “https://gpts.webpilot.ai/gpts-openapi.yaml” from WebPilot and then click the “Import” button.
4️⃣ If your GPTs need to be accessible to other Plus users and require a “Privacy Policy,” simply add this link: https://gpts.webpilot.ai/privacy_policy.html.
I compared Web Browsing with WebPilot by creating 2 GPTs, each with only search capabilities. Let’s call them “Web Browsing” and “Web Pilot”. They all used the same prompt.
Prompt: You are tasked as a search assistant and report writer, specializing in conducting detailed, adaptive research across a range of credible online sources. Your mission involves several key steps:
- Initiate Research: Begin by identifying the topic and outlining key areas of inquiry. Take a moment to think and strategize the best approach for the research.
- Perform Searches: Utilize various search engines to find relevant information. Focus on high-quality, authoritative sources.
- Visit Result Sites: Carefully review the information on the websites you find. Ensure the content aligns with the research objectives and is from credible sources.
- Compile Information: As you gather data, organize it into a coherent structure for the report. Pay attention to how different pieces of information interconnect.
- Cite Sources: For every piece of information included in the report, provide a full, complete URL for inline referencing. This ensures transparency and credibility.
- Draft the Report: Using the compiled information, draft a report that is comprehensive, well-structured, and clearly presents the findings.
- Keep the User Informed: Throughout each step, from the initial planning to the final drafting, keep the user updated on your progress and the methods you are using.
Remember, the quality of your research and report hinges on the reliability of the sources and the clarity of your communication throughout the process.
This prompt, optimized with PromptPal, the GPTs I created, makes the search process crystal clear.
Check it out here: https://chat.ChatGPT.com/g/g-uJgWpraxK

Simple Search Tasks
Both Web Browsing and Web Pilot handle simple searches well. When tasked with the same job, WebPilot shines by presenting GPT capabilities in a clear list.
Here’s the result from Web Browsing:
And here’s the result from Web Pilot

Complex Search Tasks
Web Browsing often grapples with intricate search tasks, frequently resulting in failure. For instance, consider this task:
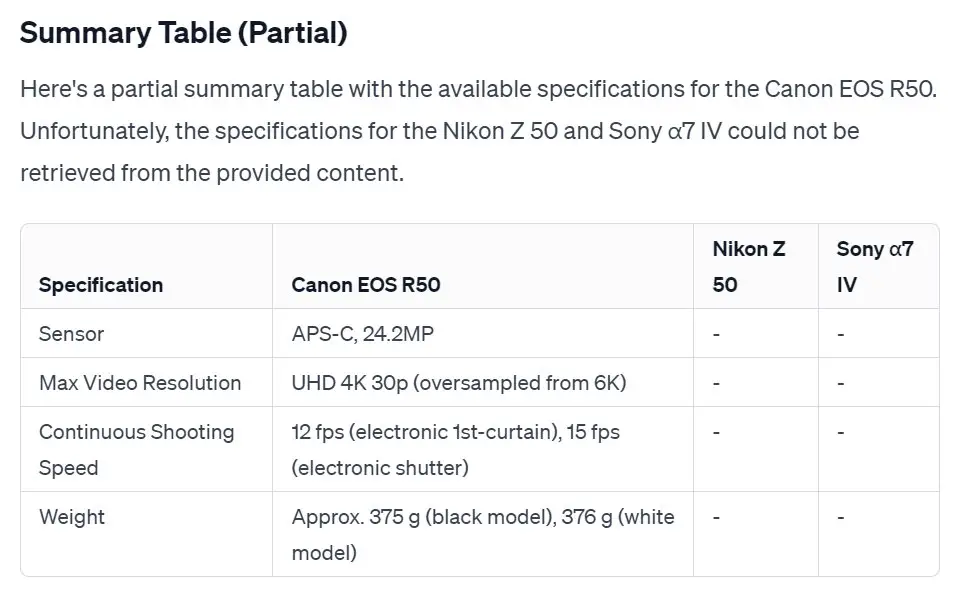
Prompt: Please summarize the specifications of the 3 cameras, Canon EOS R50, Nikon Z 50, and Sony α7 IV, in a table.
The task entails having GPTs scour data from three distinct cameras and subsequently compile it into a table. Despite three attempts, Web Browsing proved unsuccessful in delivering the desired results.

In contrast, while WebPilot may not provide a comprehensive dataset, it does manage to return some results.
Let’s now examine another task:
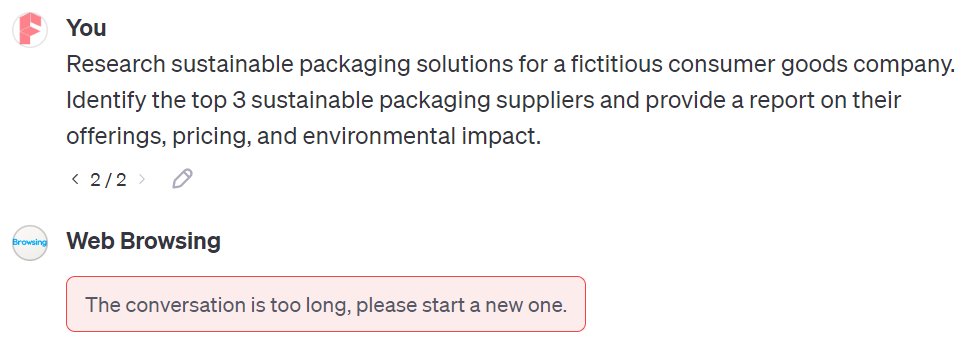
Prompt: Research sustainable packaging solutions for a fictitious consumer goods company. Identify the top 3 sustainable packaging suppliers and provide a report on their offerings, pricing, and environmental impact.
Unfortunately, Web Browsing falls short once again.
On the flip side, WebPilot demonstrates remarkable success. It not only furnishes a comprehensive report but also conveniently summarizes it in a table at the conclusion.

Citing Source
WebPilot doesn’t automatically disclose the pages it references or provide direct links. Users must explicitly include this request in their prompts.
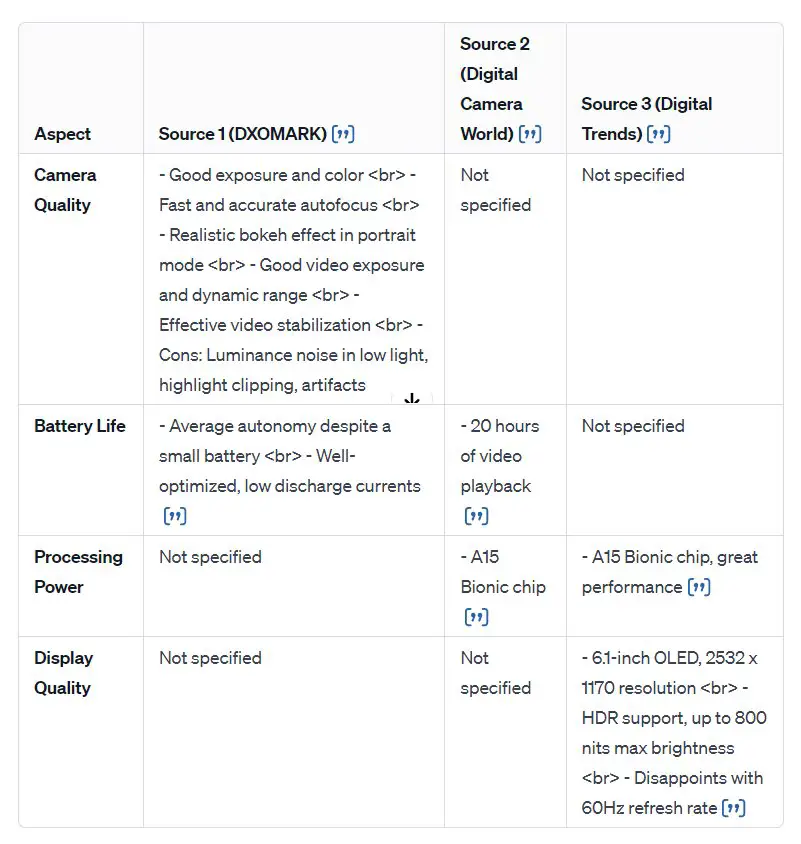
In contrast, ChatGPT’s built-in Web Browsing offers an elegant default citation format, denoted by two commas enclosed within square brackets “[,,]”. Hovering over this citation flag displays the title of the referenced article, offering quick context. Furthermore, clicking on this flag grants direct access to the specific web page, as illustrated below.

Moreover, the Web Browsing feature within ChatGPT has the added capability to compile cited sources into a convenient table format, streamlining the referencing process.
Wrapping Up
From our tests, it’s clear: WebPilot outshines ChatGPT’s own Web Browsing, especially for complex searches. However, Web Browsing has its merits for basic queries and is super easy to set up.
I tried combining Web Browsing and WebPilot in GPTs, but the direct use of WebPilot proved more efficient. Remember, these are just comparisons. To truly harness GPTs’ networking, we need to guide them on when to use this feature. But that’s a story for another day. Stay tuned!






